Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution- Here we will share Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution for icse students. Candid New Trends in Discovering the world Class 6 Solutions strictly based on the latest curriculum issued by The ICSE
Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution
queryexpress.com provides you with solutions to the latest curriculum issued by The ICSE. the solution to Candid New Trends in Discovering the world Class 6 is best for the students to acquire knowledge and prepare themselves for exams. We have solved all the questions and answers of Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution.
Apart from Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution Also, Read
- Inspired history icse class 6 solutions- Prehistory and History
- Inspired history icse class 6 question answer- Indus Valley civilisation
- Early Vedic age icse class 6 solutions
- Early Vedic age icse class 6 MCQs
Icse class 6 dreamcatcher questions and answers
- Scarecrow by Walter de la Mare
- The surprise party by J R R Tolkien
- Summary of the poem Scarecrow
- An uncomfortable bed
- The little prince question answers
- Cradle song class 6 question answers
- Cradle song class 6 summary dreamcatcher
- Big brother class 6 dreamcatcher solutions
- You are old father William class 6 dreamcatcher solution
Candid New Trends in Discovering the world Class 6 Solutions
A. Answer the following questions in brief: Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution
1. Define agriculture.
Answer- Agriculture is the science or art of cultivating the soil, growing and harvesting crops and raising livestock.
2. “Agriculture is a primary activity.” Give reason
Answer- Agriculture is a primary activity because it includes occupations which are closely related to man’s natural environment.
3. Name any three types of agriculture
Answer- Three types of agriculture are Subsistence agriculture, Intensive Agriculture and Extensive Agriculture.
4. What is shifting cultivation? By which name is it known in India?
Answer-Shifting cultivation is the type of cultivation where a small piece of forest is cleared by felling the trees, cutting the bushes and grasses and clearing the land for cultivation. It is known as jhuming in India.
5. What is commercial agriculture?
Answer- Commercial agriculture is a type of agriculture where farmers grow crops to sell in the market. The profit motive is the basis of commercial agriculture. This type of agriculture provides raw materials to agro-based industries.
6. Name any two food crops.
Answer-Rice and Wheat are two main food crops.
7. Name any two cash crops.
Answer- Cotton and Jute are the two crash crops
8. Name any two beverage crops.
Answer- Coffee and tea are two beverage crops.
9. Which state of India is the largest producer of rice?
Answer- West Bengal is the largest producer of rice in India
10. Name any two countries of the world which are the largest producers of rice
Answer- China and India are the largest producers of rice in the world.
11. Which is the largest producer of sugarcane in the world?
Answer-Brazil is the largest producer of sugarcane in the world
12. Which fibre is known as the ‘golden fibre’ of India?
Answer- Jute is known as the ‘golden fibre’ of India.
13. State the climatic condition required for the production of rubber.
Answer- The production of rubber requires a moist and humid climate with rainfall of more than 200cm, and temperature above 25 degrees.
14. Define organic farming.
Answer- Organic farming is an eco-friendly technique for growing crops without the use of harmful fertilizers and pesticides.
15. Subsistence agriculture-
Answer-it is the type of agriculture in which crops grown are consumed by the farmer and his family.
16. Commercial agriculture-
Answer-In commercial agriculture farmers grow crops to sell in the market.
17. Extensive agriculture-
Answer-It is highly mechanized farming on large farms.
18. Intensive agriculture–
Answer-Crops are grown on small land holdings by applying higher inputs of labour and capital.
Icse class 6 geography notes- Discovering the world
B. Answer the following questions in detail in Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution
1. What is the importance of agriculture? Explain
- Agriculture is the most basic form of human activity to provide food, vegetables, fruits and other basic necessities of life.
- It also produces animal products like milk, wool etc
- A large variety of agro-based industries like cotton, jute, and sugar mills depend upon agriculture for their raw materials.
- Agriculture provides employment to a large number of skilled as well as unskilled workers.
2. State any four major features of subsistence agriculture.
Answer- Agriculture Subsistence farming is a type of farming in which the crops grown are consumed by the farmer and his family. The main motive of the farmers is to satisfy the needs of their families.
- The whole family works on the farm.
- Most of the work is done manually.
- The farms are small.
- Traditional methods of farming are followed.
- The yield is not very high.
3. State any four features of extensive agriculture.
Answer- Extensive agriculture is done on large scale and most of the activities are carried out with the help of modern machinery.
The features of extensive agriculture are
- Agriculture farms are very large.
- This type of agriculture is practised in areas with a low density of population.
- Agriculture is carried out with modern machinery.
- Wheat is the major crop but barley, oats, rye and flax are also found
- This type of agriculture is found in Russia, Argentina, Australia etc.
4. Distinguish between cash crops and food crops.
| Food crops | Cash Crops | |
| 1 | Used for human consumption | Used for selling |
| 2 | Rice, wheat, and mazes are examples of major food crops. | Cotton, Jute are the example of cash crops |
| 3 | India and China are the largest producers of food crops(rice) | China, India, and Pakistan are the major producers of cash crops. (Cotton) |
5. State any four features of plantation farming.
- Plantation farming is generally raised on large estates.
- The main objective of plantation agriculture is to export products.
- Plantation agriculture is labour-intensive work. Many workers are required at each stage.
- Plantation agriculture was introduced by Europeans to meet the demand for tea, coffee cocoa, pineapple, etc.
- Tea plantations in Assam and S Lanka, rubber plantations in Malaysia and coffee plantations in Brazil are some Examples of plantation agriculture.
6. Compare rice and wheat with reference to climatic conditions and producing countries.
| Rice | Wheat | |
| 1 | India and China are the largest producers of rice in the world. | Russia, the USA, China, Canada, and France are the main producers of wheat. |
| 2 | West Bengal is the largest producers of rice in India | India is the fourth-largest producer of wheat in the world |
| 3 | Rice needs warm temperatures and is a crop of tropical climate | It is a crop of temperate regions and grows well in cool climates. |
7. What is Green Revolution? Analyse its importance for the Indian economy.
The green revolution refers to an increase in the production of food grains by using high-yielding variety(HYV) seeds.
- The spread of Green Revolution technology enabled India to achieve self-sufficiency in food grains.
- we no longer depend upon other nations, for meeting our nation’s food requirements.
- An increase in productivity increase the revenue for the farmers.
- Farmers are shifting from subsistence crops to commercial crops hence increasing growth and prosperity.
Icse class 6 geography papers chapter wise-Discovering world
D. Distinguish between
1. Subsistence agriculture and Commercial agriculture.
| Subsistence Agriculture | Commercial agriculture | |
| 1 | Crops grown are consumed by the farmer and his family | Crops grown are used for selling. |
| 2 | The motive of farmers to fulfil the needs of his family. | The motive of farmers is to earn money. |
| 3 | The farms are small | The farms are large |
| 4 | Traditional methods of farming are used | Modern methods of farming are used |
| 5 | The yield is not very high | The yield is very high |
| 6 | Most of the farming work is done manually | Farming work is done with the help of machine |
2. Intensive agriculture and Extensive agriculture.
| Intensive Agriculture | Extensive agriculture | |
| 1 | It is done on a small scale | It is done on a large scale |
| 2 | Manual farming is used | modern types of machinery are used |
| 3 | Crops are grown on a small land. | Crops are grown on large land |
| 4 | Total production is less | Total production is high |
| 5 | Best suitable in monsoon land and fertile soil | Best suitable in a cool region |
| 6 | India, China, Japan, Bangladesh and Malaysia are used intensive agriculture | Russia, Australia, and Argentina are used in Extensive agriculture. |
For Evergreen publication, books click here
Discovering the world geography class 6 solutions
E. Fill in the blanks with suitable words :
1. India And China are the leading producers of jute in the world.
2. Wheat is the main food crop of the middle latitude countries in the world.
3. Cotton is the most important fibre crop in the world.
4. Jute crop is known as the ‘golden fibre of India’.
5. Extensive agriculture is prevalent in most parts of the U.S.A.
Evergreen publication discovering the world class 6 answers
F. Match the Column A with Column B:
Rice ———————– Food Crops
Sugarcane ————– Crash Crop
Jute ———————– Golden Fibre
Green Revolution —– HYV
Organic farming ——- Sustainable Farming
Candid New trends in Discovering the world questions and answers
G Read the statement and identifies the crop.
1 It is a beverage crop and Brazil is the largest producer. (Coffee)
2. It is the most important food crop in the world. (Rice)
3. It is the most important fibre crop and needs frost-free days. (Cotton)
4. It is a tropical, as well as sub-tropical crop and Brazil, is the largest producer. (Sugarcane)
5. It is the beverage crop grown on hill slopes of Assam. (Tea)
Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution-Map reading
major producers of (a) Wheat (b) Rice (c) Jute (d) Sugarcane (e) Tea (f) Coffee
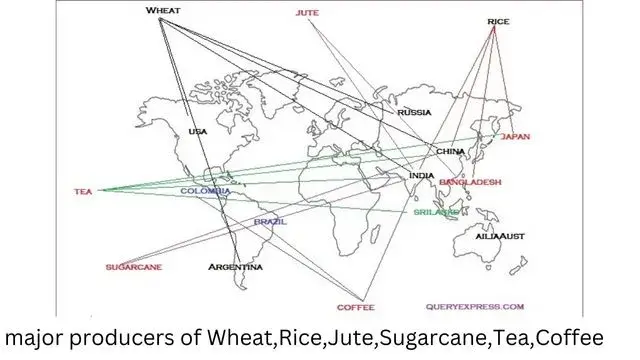
Leading producer of Crops-Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution
| Rice | India, China, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Burma, Japan | |
| Jute | India, Bangladesh | |
| Wheat | Russia, USA, China, Canada, India, France, Argentina, Australia | |
| Sugarcane | India, China, Thailand, Pakistan | |
| Tea | India, China, Japan, Indonesia, Bangladesh | |
| Coffee | Brazil, Columbia, Indonesia, Mexico, India | |
| Rubber | Thiland, Indonesia, Vietnam |
Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution and extra questions
| AGRICULTURE | |||
| CROP | Climatic Condition | Leading in the world | Leading in India |
| Rice | Tropical Climate | India and China | West Bengal |
| Wheat | Cool Climate | Russia and USA | NA |
| Maize | USA | ||
| Cotton | Tropical Climate | China | Maharastra, Tamilnadu, Gujarat, Punjab |
| Jute | Tropical Climate | India and Bangladesh | Bengal |
| Sugarcane | Tropical Climate | Brazil | |
| Rubber | Equatorial | Thiland,Indonesia and Vietnam | Kerala, Tamilnadu, Garo, Karnataka, Andaman |
| Coffee | Warm and wet climate | Brazil | Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil |
Geography Class 6 Discovering the world solution and MCQs
- ____ is the most basic form of human activity to provide food, vegetables etc. (Agriculture)
- Farming can be classified into two main types such as ____ and ____ (subsistence, commercial)
- Commercial rearing of silkworm _____ ( Sericulture)
- Breeding of fish _____ (Pisciculture)
- Cultivation of grapes ____ (Viticulture)
- Growing vegetables, flowers, and fruits are ____ (Horticulture)
- Subsistence agriculture is carried in ____, ____, ____ (Assam, Northeastern and Himalayan)
- ____ is used to fertilize the field in Subsistence farming (Animal manure)
- In tropical forests, ____ type of cultivation is followed. (Shifting cultivation)
- Shifting cultivation is called _____ in India (Jhuming)
- Shifting cultivation is followed by North-east India, the Amazon basin, Tropical Africa, and Southeast Asia.
- ___ farming is raised on large estates. (Plantation farming)
- The objective of plantation farming is ____ (export)
- Examples of plantation farming are- Rubber plantations in Malaysia, a coffee plantation in brazil, and Tea plantations in Assam and Sri Lanka.
- ____ is a labour-intensive work ( Plantation agriculture)
- ____ provides raw materials to agro-based industries. ( Commercial agriculture)
- Rice needs ___ climate. ( warm and tropical climate)
- ____ and ____ are the largest producers of rice. (India, China)
- ____ is the largest producer of rice in India. (West Bengal)
- _____ grows in a cool climate. (wheat)
- ____ is used as food and fodder. (Maize)
- ____ is the most important fibre crop in the world. (Cotton)
- Cotton is produced in India are- maharastra, Tamilnadu, Gujarat, Punjab
- ___ is called golden fibre. (Jute)
- ____ and ____ are two leading producers of jute. (India and Bangladesh)
- ____ state is the leading producer of jute in India. (Bengal)
- ____ is a tropical and subtropical crop. (sugarcane)
- Sugarcane required ____ climate. (hot and humid)
- ____ is an equatorial crop. (Rubber)
- ____ is an important industrial raw material. (Rubber)
- Which states produce rubber in India? (Kerala, Tamilnadu, Karnataka, Andaman nicobar, garo hills)
- ___ and ___ are the most important beverage crops in India. (Tea and sugar)
- Coffee requires _____ climate. ( Warm and wet climate)
- ___ is the leading producer of coffee. (brazil)
- ____ beverage crops grow on plantation farming. (Tea)
- ___ and ___ are the largest tea-producing states in India. (West Bengal and Assam)