Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions- Here we will share Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions for chapter light. Students can go through the entire content and find the solutions to Viva education physics class 6 question answers. Visit queryexpress.com to explore more from viva education, Dreamcatcher and more for class c isce students.
Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions
queryexpress.com has designed the Viva education class 6 Solutions in an easy language that gives total information regarding the syllabus of the physics book. Here we answered the entire exercise in a step-by-step process so that students can learn and prepare for their upcoming exam. Here we covered icse physics class 6 MCQs, short and long answer type questions and objective type questions and answers. By referring to this content students can acquire the concepts behind the solutions.
Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions Advantages
- Easy & step by step solutions
- it’s totally free of cost
- Explain important questions for examinations
- Solutions prepared by experts
- Prepared according to the latest ICSE syllabus.
Also, Read
- Inspired history icse class 6 solutions- Prehistory and History
- Inspired history icse class 6 question answer- Indus Valley civilisation
Icse class 6 dreamcatcher questions and answers
- Scarecrow by Walter de la Mare
- The surprise party by J R R Tolkien
- Summary of the poem Scarecrow
- An uncomfortable bed
- The little prince question answers
- Cradle song class 6 question answers
- Cradle song class 6 summary dreamcatcher
- Big brother class 6 dreamcatcher solutions
- You are old father William class 6 dreamcatcher solution
Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions- Light
Exercise
Fill in the blanks.
- We are able to see objects which are not in direct light due to the scattering of light.
- A beam of light can be parallel, convergent or divergent
- Light is a form of energy.
- A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth casts its shadow on the moon.
- A shadow is always formed on the opposite side of the light source.
- A solar eclipse occurs on a new moon day.
Icse class 6 physics solutions Viva educations
B. State whether the following statements are true (1) or false (F). Correct the false statements from Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions
- Opaque objects cast a dark shadow. (T)
- The sun and stars are artificial luminous bodies. (F) Natural
- Light travels in a straight line. (T)
- A lunar eclipse occurs on a full moon night. (T)
- A point source forms a smaller umbra and a larger penumbra region, thus giving a fuzzy shadow. (T)
- A pinhole camera forms an erect image. (F) Real image
Class 6 physics icse solutions viva education
C. Choose the correct option.
- Which of the following is an artificial luminous object? (a) Torch (b) Moon (c) Tree (d) Chair
- Which of the following is a translucent object? (a) Grease paper (b) Glass (c) Air (d) Marble
- Which of the following produces a parallel beam of light? (a) Lighthouse (b) Bulb (c) Sun (d) Candle
- Which of the following is not a characteristic of shadow? (a) It is always formed on the opposite side of the light source. (b) It is of the same size as that of the object. (c) It is always dark in colour. (d) It is of the same shape as the object.
- The size of the shadow depends on (a) the distance between the source of light and the object (b) the distance between the object and the screen (c) the size of the source of light and the object (d) all of these
- The phenomenon showing rectilinear propagation of light is/are (a) the formation of shadows (b) the occurrence of eclipses ( (c) both of these (d) none of
Viva education class 6 physics questions and answers
D. Match the columns. Column
1. Moon ————————— (d) Non-luminous body
2. Glass ————————- (a) Transparent object
3. Bulb ————————- (e) Artificial source of light
4. Beam ———————– (b) A number of rays of light
5. Pinhole camera ———– (c) Real image
Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions-Exercise
B. Give reasons
Answer-The objects which do not emit their own light are called non-luminous objects. As planets do not have their own light hence they are said to be a non-luminous body.
1. Planets are said to be non-luminous bodies.
2. A glass plate does not form a shadow.
Answer- Shadow is a dark patch formed when the path of light is obstructed by an opaque object. As glass is a transparent object through which light can pass easily. Therefore glass does not obstruct the light so a glass plate does not form a shadow.
3. Light follows a straight line path.
Answer- Due to the property of rectilinear propagation, light always follows a straight line. Light follows a straight line of the path because it is the shortest path to go from one point to another.
4. The visibility through wax paper is poor.
Answer-Wax paper is a translucent material like butter paper which blocks the path of light partially, hence visibility through wax paper is poor.
5. A pinhole camera forms a real and inverted image.
Answer- A pinhole camera is the simplest image-forming device based on the principle of rectilinear propagation of light which states that when the light comes from an object and passes through the pinhole forms its image on the other side just like a lens. As the lens produces a real and inverted image in the same way A pinhole camera also forms a real and inverted image.
Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions-Notes
C. Answer in short
1.Why is the moon considered to be a non-luminous object?
Answer– As the moon shines at night but is still considered to be a non-luminous object because the moon doesn’t have its own light. It only reflects the light of the sun and shines at the night.
2. Give uses of transparent, translucent and opaque objects.
Answer-
Transparent- it is used as a showcase, windowpanes, doors, spectacles, telescope and microscopes
Translucent- it is used as doors, windowpanes of bathrooms, clinics and offices, and laboratory equipment.
Opaque- It is used as making things where we do not want the light to pass through them. Example- wooden and metal doors, windows etc.
3. What is the nature of the beam of light produced by a lighthouse?
Answer- The nature of the beam of light produced by a lighthouse is a Divergent beam of light.
4. How are shadows formed?
Answer- A shadow is a dark patch formed when the path of light is obstructed by an opaque object. The formation of shadow occurs due to the rectilinear propagation of light.
5. What happens to the size of the umbra and penumbra when the distance between the source, the object and the screen is changed?
Answer- The size of the umbra and penumbra is changed when the distance between the source, the object and the screen is changed.
6. What do you mean by an eclipse? How many types of eclipses are formed?
Answer- Eclipse is the partial or total blocking of the light of the sun by a heavenly body. There are two types of eclipses are formed. Such as Solar and Lunar eclipses.
Physics icse class 6 viva education answers
A. Explain the following terms from Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions
1. Ray of light – The straight line of the path of light along which it moves is called the Ray of light. It is a form of energy which is diagrammatically represented by a straight line with an arrowhead. This arrowhead indicates the direction in which the ray moves.
2. Beam of light- A number of rays of light travelling together in one direction are called beams of light. A beam of light can be converging, diverging or parallel.
3. Umbra – The darker region of the shadow formed on the screen is called Umbra.
4. Penumbra – The grey zone surrounding the umbra which receives light partially is called Penumbra.
5. Rectilinear propagation of light – The property of light travelling in a straight line is called rectilinear propagation of light.
6. Shadow – A dark patch formed when the path of light is obstructed by an opaque object is called the shadow.
Viva education class 6 physics question answers
B. Differentiate between the following from Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions
1. Luminous objects and non-luminous objects
Luminous objects –Objects that emit their own light is called luminous object. These objects may be natural or artificial sources. The sun and stars are natural luminous objects whereas bulbs, candles, and tube lights are examples of artificial luminous objects.
Non-luminous objects –Non-luminous objects The object which do not emit their own light are known as non-luminous objects. These objects are visible only when they reflect light falling on them. Example- chair, table etc.
2. Solar eclipse and lunar eclipse
| SOLAR ECLIPSE | LUNAR ECLIPSE |
|---|---|
| When the moon moves in between the earth and the sun. | When the earth moves in between the moon and the sun |
| During a solar eclipse, the moon partially or fully hides the sun. | During a lunar eclipse, the earth’s shadow partially or fully hides the moon. |
| A solar eclipse happens on a new moon day | A lunar eclipse happens on a full moon day. |
| A solar eclipse happens on a new moon day. | Two lunar eclipses happen in a year. |
| It can be viewed from a small area of the earth. | It may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of the earth. |
| The solar eclipse lasts for a few minutes. | The lunar eclipse lasts for a few hours |
3. Broad source and a point source of light by giving diagrams of shadows formed by them
Broad source of light
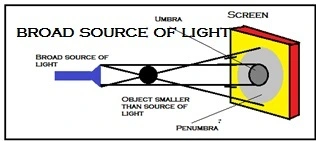
- The shadow formed on the screen has two regions.
- The darker region is Umbra and the grey region is Penumbra.
- The broad source of light forms smaller umbra and larger penumbra
Point source of light
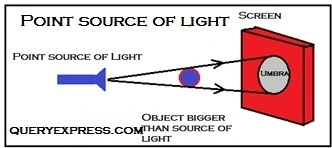
- The shadow formed on the screen has only one region.
- The shadow formed is uniformly dark, sharp and of the same shape.
- The point source of light forms a large umbra
4. Transparent objects and opaque objects
Transparent objects-
- A medium or object which allows light to pass through it completely is called a transparent object.
- An object is clearly visible when viewed through a fully transparent medium
- Uses of transparent objects are making of showcases, windowpanes, doors, spectacles etc
Opaque objects-
- A medium or an object which does not allow light to pass through it is called an Opaque object.
- It always cast its shadow when placed in the path of light.
- Uses of opaque objects are for making wooden and metal doors, brick walls etc.
Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions for chapter Light.
C. Answer in detail from Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions
1.Explain the scattering of light.
Answer- The deflection of light from its straight path by particles of a medium such that some of the light is absorbed and re-emitted in different directions is called scattering of light. Due to the scattering of light, we are able to see objects which are not in the direct path of sunlight. Our atmosphere appears bright due to the scattering of light. We can see dawn and dusk time due to the scattering of light.
2. Differentiate between transparent, translucent and opaque objects on the basis of the amount of light they allow to pass through and the shadow formed by them.
Answer-icse class 6 physics chapter Light exercise
Transparent Material
A medium or an object which allows light to pass through it completely is called a transparent medium or transparent object. Examples are glass, air and water. • An object is clearly visible when viewed through a fully transparent
Translucent Material
A medium or an object which allows light to pass through it only partially is termed a translucent medium or translucent object. Examples are wax paper, frosted glass, coloured bottles and fog. Visibility through a translucent medium is poor.
Opaque Material
A medium or an object which does not allow light to pass through it is known as an opaque medium or opaque object. Examples are wooden doors, metal, books and brick walls. An opaque object always casts its shadow when kept in the path of light.
3. Give one experiment that confirms that light travels in a straight line.
Answer-
To prove the property of rectilinear propagation of light that means light travels in a straight line. for this experiment, we need A long straw and a small source of light (led)
Procedure- Hold the straw straight in front of the source of light such that one end of the straw is towards the source.
Now Look at the source of light through the other end of the straw. You will be able to see the light when the straw is straight. Now bend the straw and then try to look through it. you will not be able to see the light anymore when the straw is bent. Hence it is proved that light travels in a straight line.
4. Define a beam of light and explain its types with the aid of diagrams.
Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions pdf
When a number of rays travel together in one direction, they are collectively known as a beam of light. A torch produces a beam of light. A beam of light can be parallel, converging or diverging.
Parallel beam: When a number of rays move parallel to each other, the beam is called a parallel beam of light. It is produced by a distant source of light like the sun.
Convergent beam: A collection of rays of light coming from different directions which converge or meet at a single point is called a convergent beam of light. Sunlight passing through a magnifying lens is an example of a convergent beam.
Divergent beam: The rays of light emitted by a small (point) source which travels in different directions form a divergent beam of light. Light emitted by a bulb, an LED, a candle or a lighthouse are examples of divergent beams.
Chapter Light-Icse physics class 6 Viva education solutions
5. Write a note on the formation of shadows.
Answer-A shadow is a dark patch formed when the path of light is obstructed by an opaque object. The formation of the shadow is a direct consequence of the rectilinear propagation of light. This is because an opaque substance does not allow light to pass through it hence it casts a dark shadow opposite of the object.
6. What is a solar eclipse? Explain with the help of a neat diagram.
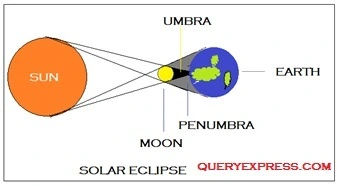
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon during its course of revolution passes between the sun and the earth and the three heavenly bodies position themselves in a straight line. The moon fully or partially covers the sun, as viewed from some parts of the earth. Since the light from the sun is blocked by the moon, the shadow of the moon falls on the earth and it becomes dark during the daytime. A solar eclipse occurs only on a new moon day.
7. What happens during a lunar eclipse? Explain the types of lunar eclipses with the help of a neat diagram.
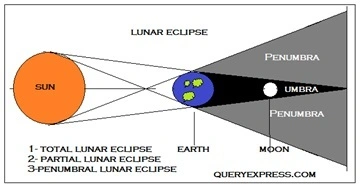
A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth comes in between the sun and the moon and its shadow falls on the moon. Due to this the moon is not visible for some time and remains hidden. This phenomenon is called the Lunar eclipse.
1. Total lunar eclipse: When the moon is completely in the umbra region of the earth, it does not receive any light and hence is not visible to the people on the earth. This is called a total lunar eclipse.
2. Partial lunar eclipse: During its course of revolution around the earth when the moon moves in the penumbral region of the earth’s shadow, it receives some light from the sun, which it reflects back to the earth. Thus the moon becomes partially visible and this is known as a partial lunar eclipse.
3. Penumbral lunar eclipse: When the moon passes through the earth’s penumbra, it experiences a penumbral lunar eclipse.
8. Explain how an image is formed by a pinhole camera. Mention the characteristics of the image formed.
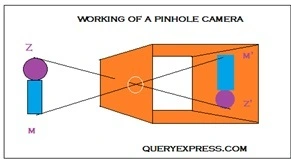
Answer-When a ray of light coming from point Z travels along ZO, passes through the pinhole O and finally falls on the screen at Z’. Similarly, a light ray coming from point M travels along MO, passes through the pinhole O and falls on the screen at M’. All the other rays which start between Z and M pass through the pinhole and fall on the screen between Z’ and M’. While passing through the pinhole, the light rays intersect and cross over. Thus, the final image M’Z’ is formed which is an inverted image of the object ZM.
Characteristics of the image formed by a pinhole camera-
- The image formed is inverted.
- The image is real as it can be obtained on the screen.
The size of the image depends on two factors.
(a) The distance between the pinhole and the screen
(b) The distance between the object and the pinhole
9. Write the advantages and disadvantages of a pinhole camera.
Advantages of a Pinhole Camera
• There is no need for focusing.
• Since there is no lens used in a pinhole camera, the image obtained is free from optical defects like colour distortion.
Disadvantages of a Pinhole Camera
• The image is obtained on a screen and no permanent record of the image can be maintained.
• The image formed lacks sharpness and is faint. No details can be observed in it.
• An image of a moving object cannot be captured using a pinhole camera. It only forms images of stationary objects.
