icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world- here we will give you the best solutions to chapter 1 “Representation of geographical features” of icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world. students can read the entire solutions to “Representation of geographical features” carefully for their upcoming exam.
Click below to read more
Chapter-1 (Representation of geographical features
Chapter-2 ( landforms)
icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world-Syllabus
- Scarecrow by Walter de la Mare
- The surprise party by J R R Tolkien
- Summary of the poem Scarecrow
- An uncomfortable bed
The syllabus of icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world contains
- Representation of Geographical features
- Landforms
- (a )water bodies (oceans and seas)
- (b)Water bodies (Lakes and Rivers)
- Agriculture
- Minerals
- (a)Study of Continents(North America)
(b) Study of Continents (South America)
Also Read,
- Plant life chapter 1 icse class 6
- Plant life chapter 1 icse class 6 long answer
- Plant life Chapter 1 ICSE class 6-extra question
- Inspired History class 6 question answer orient BlackSawn
icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world question answers
A. Answer the following questions in brief :
1. Define the map.
Answer- A map is a flat, symbolic representation of the earth or a part of the earth’s surface and it is drawn to a scale.
2. Write any three basic elements of a map.
Answer- The three basic elements of maps are distance, directions and symbols
3. Which colour would you use to show the following on a map
Answer-
(a) Mountains —— Brown
(b) Lesser depth of water —- Light blue colour
4. What is a compass?
Answer-A compass is a device that shows the direction. It consists of a magnetic needle that always points north and south when it’s at rest.
5. “A map is not an accurate representation of the earth”. Justify.
Answer-
6. Define scale.
Answer- A scale is a ratio between a unit distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground.
7. What is the difference between a map and a sketch?
Answer- Maps are drawn in scale but sketches are not drawn according to scale. it is drawn in free hand.
8. Name the four cardinal points.
Answer- the four cardinal points are North, East, South and West
9. What is cartography?
Answer- Cartography is the study of making and using maps.
10. Who was Ptolemy?
Answer- Ptolemy was an Egyptian mathematician who gave the idea of latitude and longitude.
11. What are conventional signs?
Answer- the signs that are used on a map is called Conventional Signs. Conventional signs are the colour, and symbol that shows various details on a map.
12. What is the importance of the grid system?
Answer- A grid system is used to find the exact location of a place on a map.
icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world solutions
B. Answer the following questions in detail :
1. What are the major types of maps? Explain.
Answer-
Small scale maps- these maps represent large areas of the earth. The purpose of such maps is to show a small amount of detail about a large area. Ex-Atlas map
Large scale map- These maps show a large number of details about a small area. Ex-road map, city map
Political maps– maps that show the boundaries and areas of different countries and states are called political maps. these are also a small-scale map that shows the capital, cities and other important towns.
Physical map- these maps show the physical features like oceans, continents, mountains and plains
Thematic maps- these maps are used to represent only particular features such as types of weather, industries, forest, people and minerals.
2. “Maps are useful tools.” Explain.
Answer- maps are useful tools because it is effective means of showing the location of a place. it is used to provide details of a place like its topography and climate. And maps are also used to represent many characteristics of an area, shape, direction and distance.
3. What is a scale? Explain the two common types of scales.
Answer- A scale is a ratio between a unit distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. There are two common types of scales which are used to represent distances.
Linear scale- it consists of a straight line, drawn to scale, which is divided conveniently in terms of distance on the earth.
Representative fraction- in this method the map scale is expressed as a numeric ratio. The denominator represents the corresponding ground distance.
4. “Key or symbols reveals the story of a map”. Analyse the statement.
Answer-
icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world notes
C. Define :
(a) Delta-
Answer- A triangular piece of land that develops at the mouth of a river by deposition of sediments.
(b) Tributary
Answer- A tributary is a smaller river or stream that joins a large river.
(c) Distributary –
Answer- it is a river or a stream which flows away from a large river.
(d) Block Mountain
Answer- Block Mountains are created when large areas are broken and displaced vertically. The uplifted blocks are called horst and the lowered blocks are called graben.
(e) Anticline
Answer-The upfolds in the rocks due to the folding of rocks are called Anticline.
(f) Syncline
Answer- The downfolds in the rocks due to the folding of rocks are called syncline.
(g) River
Answer- A river is a body of flowing water.
Representation of geographical features chapter 1 class 6 question answers
D. Mark True (T) or False (F) against the statements given below :
1. A sketch is drawn exactly to scale. (F)
2. A plan is a large-scale map. (T)
3. The north is shown on the right-hand side of a map. (F)
4. Scale of the map helps in measuring the actual distances between various places shown On a map. (T)
5 Maps are sometimes drawn without a scale. (F)
6. A map can show even a small part of the earth. (T)
Representation of geographical features chapter 1 class 6 solutions
E. Give a single term for each of the following
1. A model of the earth of small size.—- Globe
2. Lines on the maps showing the height of places above the sea level— Contour lines
3. A map showing the boundaries of countries and states. — Political map
4. A map on a very large scale. —- Large-scale map
5. A rough drawing not drawn to scale. — Sketch
icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world-Chapter 1
F. Match the following :
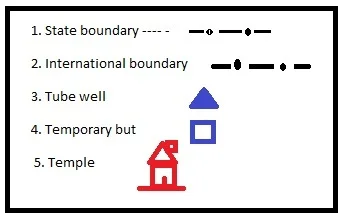
G. Select the correct answer from those given below each of the statements.
1. Which of the following is a true representation of the earth as a whole? – Globe
2. Which of the following is not made to scale?— Sketch
3. What is shown with the help of contour lines on maps?— Height
4 Which of the following, will have the largest scale?— A city guide map
5 The map showing the boundaries and areas of different countries and states is called— political map
Features of a map-icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world
- Maps provide information about far-off countries.
- Maps show the rivers, mountains and roads.
- The map shows the natural conditions, climate, and vegetation of a particular area.
- Maps are extremely useful for defence purposes.
icse class 6 geography-New trends in Discovering the world MCQs
- A _____ is a map which is drawn at a very large scale. (plan)
- The science of map making is called ______(cartography)
- ______ are used to show different features on maps(conventional sign)
- _____ represents large areas of the earth. (small scale map)
- ______ shows a large number of details about a small area. (Large scale map)
- The temperature of various places is shown on the map by lines joining places with the same temperature are called ______( isotherms)
- Lines which join places of the same height are called ______ lines. (contour lines)
- The shape of earth is called ________( Geoid /sphere)
- ______ is a three-dimensional scale model of the earth. (Globe)
- ____ is a true model of the earth. (Globe)
- A _____ is a 3D software model or representation of the earth or another world. ( virtual globe)
- A ____ is a flat, symbolic representation of the earth or a part of the earth’s surface. ( Map)
- ______ is the proportion between the actual or ground distance or map distance. (scale)
- ______ are used to provide details of a place like its topography, climate etc. (map)
- Maps showing the boundaries and areas of different countries and states are called ___ (Political map)
- Political maps are _____ maps (small sale maps)
- Maps that show the ocean, plateaus, and continents are called _____ ( physical map)
- Maps that represent only particular features like weather, forests, industries, people, and minerals are called ______ (Thematic map)
- The four major directions are called _____ (Cardinal points)
- A ______ is an instrument that shows direction. ( Compass)
- _____ or _____ tells the story of the map. ( key / symbols)
- Maps are only _______ dimensions. ( two dimensions)
- _______ is used to show the height of land and the depth of the sea. ( Colour)
- ______ Colour is used to show mountains. ( brown)
- _______ Colour is used to show the lesser depth of the sea. (light blue)
- ______ Colour is used to show deeper areas. ( dark blue)
- In this method, the map scale is expressed as a numeric ratio. ( Representative fraction)
- ______ is a set of lines used to find the exact location of a place on a map. ( Grid system)
- _____ are imaginary circular lines running parallel to the equator. (Lines of Latitude)
- _____ are the imaginary lines that bisect the globe through the north and south. ( Longitude)
- Maps that are not drawn according to scale are called ____ ( Sketch)
- _____ is a body of flowing water. (river)
- A _____ is a winding curve in a river formed as a result of depositional and erosional processes. (meander)
- A ______ is a smaller river or stream that joins a large river. ( Tributary)
- ______ is a river or stream which flows away from a large river. ( Distributary)
- _______ is a triangular piece of land that develops at the mouth of a river by deposition of sediments.
- _______ are created when large areas are broken and displaced vertically. (Block mountains)
- _____ is a process that produces folds and bends in rock. ( Folding)
- The upfolds in the rocks are called _______ (anticlines)
- The downfolds in the rock are called _____ (synclines)