Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Exercise Solutions-Here, we will share Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Exercise Solutions. If you are searching for Class 6 Science Chapter Diversity in the Living World Exercise Solutions, you are at the right place. queryexpress gives the best solutions to Class 6 Science Curiosity.
Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Exercise Solutions
Also, Read
- Measurement of Length and Motion Class 6 Notes
- Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Notes
- Wonderful World of Science Class 6 Chapter 1 MCQs
- The Wonderful World of Science Class 6 Notes
- Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Chapter 2 MCQs
- Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Extra Questions
- Locating Places on the Earth Class 6 Chapter 1 Notes
- Materials Around Us Class 6 Notes and MCQs
- Materials Around Us Extra questions and answers
Diversity in the Living World Exercise Solutions,
Exercise Questions and Answers
1. Differences Among Roots and Leaf Venation of Wheat and Kidney Beans:
(a) Wheat:
- Type of Root: Fibrous root system, where many roots of similar size spread out from the base of the plant.
- Leaf Venation: Parallel venation, where the veins in the leaf run parallel.
(b) Kidney Beans:
- Type of Root: Taproot system, where one main root grows deep into the soil with smaller roots branching off.
- Leaf Venation: Reticulate venation, where the veins form a net-like pattern.
2. Grouping Animals Based on Their Habitats:
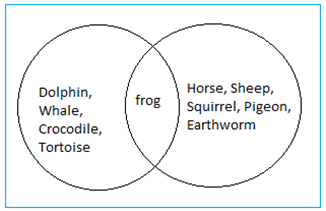
- Aquatic Animals (A): Dolphin, Whale, Crocodile, Tortoise
- Terrestrial Animals (B): Horse, Sheep, Squirrel, Pigeon, Earthworm
- Animals Living in Both Habitats (C): Frog
3. Type of Root and Venation in Radish:
- Type of Root: Radish has a taproot system, where the main root grows deep into the soil, storing nutrients.
- Type of Leaf Venation: The radish plant has reticulate venation in its leaves, where the veins form a network.
4. Similarities and Differences Between Mountain Goat and Plains Goat:
Similarities:
- Both are goats and belong to the same general species.
- Both have hooves, and horns and are herbivores.
Differences:
- Mountain Goat: Has thicker fur, more muscular legs, and specialized hooves that provide grip on rocky surfaces.
- Plains Goat: Has shorter fur and is adapted to more level terrains with softer ground.
Reasons for Differences:
- These differences are due to their habitats. Mountain goats are adapted to colder, rocky environments, requiring thicker fur and better grip. Plains goats, on the other hand, live in warmer, flatter areas where such adaptations are unnecessary.
5. Grouping Animals Based on a Different Feature:
Feature: Mode of Movement
- Flying Animals: Pigeon, Bat, Cockroach, Grasshopper
- Non-Flying Animals: Cow, Tortoise, Whale, Fish, Lizard
6. Effects of Deforestation and Possible Solutions:
Effects:
- Loss of Biodiversity: Deforestation leads to the loss of habitats for many species, causing them to become endangered or extinct.
- Climate Change: Trees absorb carbon dioxide, and cutting them down increases greenhouse gases, leading to global warming.
- Soil Erosion: Without trees, the soil becomes loose and is easily washed away, reducing fertility.
Solutions:
- Reforestation: Planting trees to replace those that were cut down.
- Sustainable Living: Reducing the use of wood and paper products, and recycling.
- Protected Areas: Creating and maintaining reserves and national parks to protect forests and wildlife.
7. Flowchart Analysis:
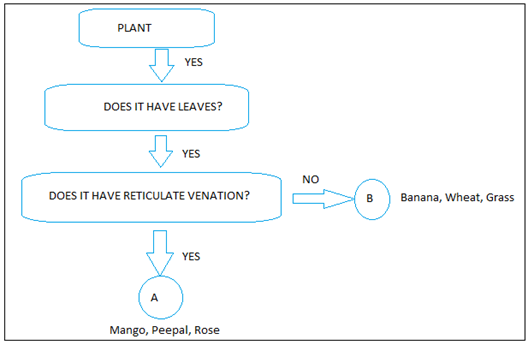
- Examples of ‘A’ (Reticulate Venation): Mango, Peepal, Rose
- Examples of ‘B’ (Parallel Venation): Banana, Wheat, Grass
8. Questions Sanjay Can Ask About the Gudhal (Hibiscus) Plant:
- What are the characteristics of a shrub?
- How tall does the Gudhal (Hibiscus) plant grow?
- Does it have multiple woody stems or just one main stem?
- How long does the Gudhal plant live?
9. Based on the information in the table, find examples of these plants for each group.
| Group | Type of seed | Type of root | Examples |
| A | Dicot | Taproot | Mango, Pea, Rose, Mustard |
| B | Monocot | Fibrous roots | Wheat, Rice, Maize, Bamboo |
(a) What other similarities do plants of group A have?
Answer-Plants in Group A (Dicots) typically have reticulate venation in their leaves, where the veins form a network-like pattern.
(b) What other similarity do plants of group B have?
Answer-Plants in Group B (Monocots) typically have parallel venation in their leaves, where the veins run parallel.
10. Differences in Duck’s Feet:
- Difference: Ducks have webbed feet, where the toes are connected by skin.
- Activity: The webbed feet help ducks swim efficiently in water, making them excellent swimmers compared to other birds that do not have webbed feet.
10. Indian Scientists Working on Biodiversity:
Divya Mudappa, Vidya Athreya, and Uma Ramakrishnan are some notable scientists working to protect India’s biodiversity. Each focuses on different aspects, such as wildlife conservation, understanding species’ genetic diversity, and human-wildlife conflict resolution.