Dav Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes-Here, we will share Dav Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes- Changes around us. If you are searching for Class 6 Science Changes around us notes for Dav students, then you are at the right place. queryexpress provides the best solutions to Dav public School Science notes.
Dav Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes- Changes around us
| SL.NO | TOPIC |
| 1 | Our Environment |
| 2 | Food |
| 3 | Nature of matter |
| 4 | Separation of Substance |
| 5 | Changes around us |
| 6 | Measurement and Motion |
| 7 | The world of living |
| 8 | Structure and Function of the Living Organism-Plants |
| 9 | Structure and Function of the Living Organism-Animals |
| 10 | Work and Energy |
| 11 | Electric currents and Circuits |
| 12 | Light and Shadows |
| 13 | Magnents |
| 14 | Electric Currents and Circuits |
Dav Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Notes- Changes around us
Overview
Change is a fundamental aspect of nature and life. Everything around us is constantly undergoing change—some visible, some invisible. Understanding the types of changes helps us make sense of natural phenomena, human activities, and scientific processes.
Change is a constant phenomenon in our surroundings. Everything—from natural events to human activities—undergoes change. These changes can affect:
- Shape
- Size
- Position
- Composition
Examples include:
- Melting of ice
- Growth of plants
- Evaporation of water
- Day and night cycles
- Seasonal changes
Types of Changes

1. Slow and Fast Changes
Slow Changes
These occur gradually over a long period of time. They are often hard to notice immediately but become evident over days, months, or years.
Examples:
- Growth of a plant or human
- Rusting of iron
- Formation of soil from rocks
- Change of seasons
Scientific Insight: Slow changes often involve biological or geological processes. For example, rusting is a chemical reaction between iron, water, and oxygen forming iron oxide.
Fast Changes
These happen quickly and are often dramatic or sudden.
Examples:
- Bursting of a balloon
- Lightning during a storm
- Cutting vegetables
- Switching on a light bulb
Scientific Insight: Fast changes may involve physical actions or rapid chemical reactions. For instance, lighting a bulb involves the flow of electric current, which instantly produces light.
Class 6 Dav Science Chapter 5 Changes around us notes
2. Reversible and Irreversible Changes
Reversible Changes
These changes can be undone or reversed. The original substance or state can be recovered.
Examples:
- Melting and freezing of ice
- Inflating and deflating a balloon
- Dissolving salt in water (can be recovered by evaporation)
- Stretching rubber
Scientific Insight: Reversible changes usually involve physical changes in state or form, without altering the chemical composition.
Irreversible Changes
These changes cannot be undone. A new substance is often formed, and the original cannot be recovered.
Examples:
- Burning of paper
- Cooking food
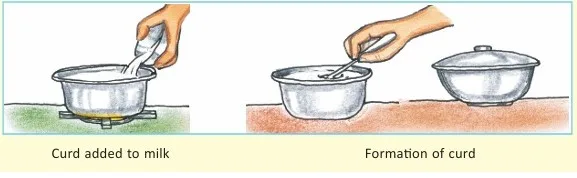
- Curdling of milk
- Rusting of iron
Scientific Insight: Irreversible changes often involve chemical reactions. For example, burning paper produces ash, carbon dioxide, and water vapor—none of which can be turned back into paper.
Changes around us Class 6 Dav Science notes
3. Physical and Chemical Changes
Physical Changes
Only the physical properties (like shape, size, state) change. No new substance is formed.
Examples:
- Melting of wax
- Boiling water
- Breaking glass
- Folding paper
Key Features:
- Reversible in most cases
- No change in chemical composition
- Energy may be absorbed or released
Chemical Changes
A new substance is formed with different properties. These changes are usually irreversible.
Examples:
- Burning wood
- Making curd from milk
- Rusting of iron
- Digestion of food
Key Features:
- Involves chemical reactions
- Often irreversible
- Change in smell, color, temperature, or formation of gas may occur
Scientific Insight: Chemical changes involve breaking and forming of chemical bonds. For example, when milk turns into curd, bacteria convert lactose into lactic acid.
Dav Public school Class 6 Science notes
Energy and Change
Every change involves energy. It may be:
- Absorbed (endothermic)
- Released (exothermic)
Energy Absorbed
- Melting ice (heat absorbed)
- Boiling water
- Photosynthesis (plants absorb sunlight)
Energy Released
- Burning fuel
- Respiration (energy released in cells)
- Fireworks
Scientific Insight: Energy changes are crucial in understanding whether a change is physical or chemical. Chemical changes often release or absorb more energy than physical ones.
Summary of Key Concepts
- Changes are all around us and can be classified based on speed, reversibility, and nature.
- Slow vs Fast: Based on time taken.
- Reversible vs Irreversible: Based on whether the original state can be restored.
- Physical vs Chemical: Based on whether a new substance is formed.
- Energy plays a vital role in driving changes.
Important Terms
| Term | Definition |
| Physical Change | Change in physical properties without forming a new substance |
| Chemical Change | Formation of a new substance with different properties |
| Reversible Change | Can be undone or reversed |
| Irreversible Change | Cannot be undone |
| Slow Change | Takes place over a long time |
| Fast Change | Happens quickly |
| Energy Change | Involves absorption or release of energy |
Changes around us class 6 notes
Real-Life Applications
- Cooking: Combines physical and chemical changes (e.g., boiling water vs frying an egg)
- Weather: Fast changes (storms) and slow changes (climate shifts)
- Industry: Chemical changes used in manufacturing (e.g., making cement, steel)
- Biology: Growth, digestion, respiration—all involve irreversible chemical changes
Chapter 5: Changes Around Us
Types of Changes
1. ⏳ Slow and Fast Changes
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Slow Change | Takes place over a long duration | Growth of a plant, rusting of iron, change of seasons |
| Fast Change | Happens quickly or instantly | Burning paper, cutting an apple, lighting a bulb |
Activity Examples:
- Curdling milk slowly with curd (slow)
- Making cheese quickly with lemon juice (fast)
2. Reversible and Irreversible Changes
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Reversible | Can be undone or reversed | Freezing/melting water, stretching rubber, switching a bulb on/off |
| Irreversible | Cannot be undone | Burning paper, making curd, aging, cooking food |
Activity Examples:
- Ice melting and refreezing (reversible)
- Burning paper into ash (irreversible)
3. Physical and Chemical Changes
| Type | Description | Examples |
| Physical Change | No new substance is formed; only appearance or state changes | Melting ice, tearing paper, bending wire, glowing bulb |
| Chemical Change | A new substance is formed with different properties | Burning wood, curdling milk, rusting iron, cooking food |
Activity Examples:
- Grinding sugar (physical)
- Heating sugar until it turns brown and bitter (chemical)
Changes Involve Energy
Changes are often accompanied by energy transformations:
Energy Released
- Burning candle
- Respiration
- Combustion of LPG
Energy Absorbed
- Melting ice
- Boiling water
- Moving a cricket ball
Summary Points (You Must Know)
- Changes are everywhere—in nature and in daily life.
- They can be slow/fast, reversible/irreversible, physical/chemical.
- Reversible changes can be undone; irreversible ones cannot.
- Physical changes don’t form new substances; chemical changes do.
- Energy is either released or absorbed during changes.
Changes around us class 6 Dav science MCQS
- A change that takes place slowly over time is called a slow change.
- Burning of paper is an example of a chemical change.
- Melting of ice is a reversible and physical change.
- A change in which a new substance is formed is called a chemical change.
- Rusting of iron is a slow and chemical change.
- Dissolving salt in water is a reversible and physical change.
- A change that cannot be reversed is called an irreversible change.
- Stretching a rubber band is a reversible and physical change.
- Cooking food is an example of a chemical and irreversible change.
- Changes that happen quickly are called fast changes.
- Changes that happen over a long period are called slow changes.
- Energy is absorbed or released during a change.
- Lighting a bulb is a fast and physical change.
- Making curd from milk is a chemical and irreversible change.
- Breaking a glass is a fast and physical change.
