DAV Class 6 Science Chapter 1 notes-Here, we will share DAV Class 6 Science Chapter 1 notes. If you are searching for DAV Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Our Environment notes, then you are at the right place. queryexpress provides the best notes on DAV Public School Class 6 Science Chapter 1 notes
DAV Class 6 Science Chapter 1 notes-Our Environment
| SL.NO | TOPIC |
| 1 | Our Environment |
| 2 | Food |
| 3 | Nature of matter |
| 4 | Separation of Substance |
| 5 | Changes around us |
| 6 | Measurement and Motion |
| 7 | The world of living |
| 8 | Structure and Function of the Living Organism-Plants |
| 9 | Structure and Function of the Living Organism-Animals |
| 10 | Work and Energy |
| 11 | Electric currents and Circuits |
| 12 | Light and Shadows |
| 13 | Magnents |
| 14 | Electric Currents and Circuits |
DAV Class 6 Science Chapter 1 notes
Detailed Notes on DAV Class 6 Science Chapter 1: Our Environment
I. Components of the Environment
Our environment is made up of two main components:
- Biotic Components (Living): This includes all living organisms, such as plants, animals, and humans.
- Abiotic Components (Non-Living): These include non-living elements such as air, water, soil, light, and temperature.
II. Biotic Environment: The Living World
- Plants (Producers): Plants are also called producers or autotrophs because they prepare their own food. They use a process called photosynthesis, which uses chlorophyll to absorb sunlight and convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- Animals (Consumers): Animals are called consumers or heterotrophs because they cannot prepare their own food and depend on plants for it. They are categorised based on their diet:
- Herbivores (Primary Consumers): These animals directly eat plants, such as cattle and goats.
- Carnivores (Secondary Consumers): These animals feed on other animals (herbivores), like tigers and lions.
- Omnivores: These animals eat both plants and other animals, such as bears, pigs, and humans.
- Scavengers: These animals, like jackals, crows, and vultures, consume the dead bodies of other animals, which helps keep the environment clean.
- Micro-organisms (Decomposers): These are organisms like fungi and bacteria that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. They are called decomposers because they get their food from dead and decaying plants and animals. They break down these dead organisms into minerals, which then mix with the soil and are reused by plants. This process is known as the recycling of minerals.
DAV Class 6 Science Chapter 1 notes- Our Environment
III. Abiotic Environment: Non-Living Factors
Abiotic components are essential for the survival and growth of living organisms.
IV. Interaction in the Environment
- Food Chain: This is a sequence in nature where one organism eats another, which in turn is eaten by another, and so on. For example, grass is eaten by a deer, which is then eaten by a lion.
- Mineral Cycle: This is the continuous cycling of materials between the biotic and abiotic components of the environment. Decomposers play a crucial role by returning nutrients from dead organisms to the soil, which are then used again by plants.
DAV Public School Class 6 Science Chapter 1 notes
V. Waste Management
The chapter also discusses the importance of waste management based on whether materials can be broken down naturally:
- Biodegradable Materials: These materials, like paper and cloth, can be broken down into simpler substances by microorganisms.
- Non-biodegradable Materials: These materials, such as plastic, cannot be decomposed by microorganisms and can harm the environment.
- Vermicomposting: This is the process of making compost from kitchen waste using worms, particularly redworms.
DAV Class 6 Science Our Environment Notes Important Questions
Fill in the blanks
- The two main components of the environment are biotic and abiotic.
2. Living organisms, including plants, animals, and humans, form the biotic components.
3. Non-living things like air, water, and soil are called abiotic components.
4. Green plants are known as producers because they make their own food.
5. The process by which plants prepare food is called photosynthesis.
6. The green colouring matter in the leaves of plants is called chlorophyll.
7. Animals that eat only plants are called herbivores or primary consumers.
8. Animals that feed on other animals are called carnivores.
9. Animals that eat both plants and other animals are called omnivores.
10. Organisms that feed on dead and decaying plants and animals are known as decomposers.
11. Fungi and bacteria are examples of microorganisms that act as decomposers.
12. The process of breaking down dead organisms into minerals that go back into the soil is called the recycling of minerals.
13. The sequence of one organism eating another is called a food chain.
14. The balance of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere is maintained by photosynthesis and respiration.
15. Rainwater harvesting is a method of collecting and storing rainwater for later use.
16. Materials that can be decomposed by microorganisms are called biodegradable materials.
17. Plastic and glass are examples of non-biodegradable materials.
18. The process of preparing compost from kitchen garbage using redworms is called vermicomposting.
19. A scavenger is a bird or animal that feeds on the dead bodies of other animals.
20. The cycling of materials through biotic and abiotic components is known as the mineral cycle.
Notes on Our Environment Class 6 Dav Chapter 1
Dav class 6 science chapter 1 notes-Give Reason
Give reason: Green plants are also called producers.
- Answer: Green plants are called producers because they can prepare their own food using a process called photosynthesis, which uses sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
Give reason: Decomposers are important for the environment.
- Answer: Decomposers are important because they break down dead and decaying plants and animals, returning essential minerals to the soil. This process, known as the recycling of minerals, ensures that nutrients are available for new plants to grow.
Give reason: It is important to segregate biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste.
- Answer: It is important to segregate these wastes because biodegradable materials can be broken down naturally and converted into compost, while non-biodegradable materials like plastic cannot be decomposed by microorganisms and can cause harm to the environment.
Give reason: Scavengers are helpful in cleaning the environment.
- Answer: Scavengers, such as vultures and jackals, help clean the environment by feeding on the dead bodies of other animals. This prevents the accumulation of carcasses and the spread of disease.
Give reason: A food chain is a crucial part of an ecosystem.
- Answer: A food chain is crucial because it shows how energy is transferred from one organism to another. It demonstrates the interdependence of living organisms and how they rely on each other for survival.
Activity-based questions and answers on Dav class 6 science chapter 1 notes
Based on Activity 1, help the zoo feeder categorise the following animals into the correct groups: lion, deer, bear, and kangaroo.
- Answer:
- Herbivores: Deer, Kangaroo
- Carnivores: Lion
- Omnivores: Bear
Based on Activity 2, a student buries a plastic bag, a piece of cloth, and a newspaper in the soil. After one month, why does the plastic bag show no change while the paper and cloth are partially decomposed?
- Answer: The plastic bag shows no change because it is a non-biodegradable material. It cannot be broken down by microorganisms. The paper and cloth are biodegradable materials, which means they can be broken down into simpler substances by microorganisms, causing them to decompose.
Based on Activity 3, you are asked to categorise waste items you throw away. What are the three categories, and why is this activity important?
- Answer: The three categories are recycled, reused, and composted. This activity is important because it helps us to handle waste in an environmentally friendly way by segregating biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste.
Based on Activity 4, why is creating a poster on “Harvest Water to Harness Life” a good idea?
- Answer: A poster on “Harvest Water to Harness Life” is a good idea because rainwater harvesting helps to supplement the water requirement of cities and raise the sub-soil water level. This, in turn, helps maintain and increase greenery in urban areas.
Based on Activity 5, arrange the following words to form a terrestrial food chain: rat, owl, snake, grass, grasshopper.
- Answer: A terrestrial food chain can be formed as follows:
- Grass -> Grasshopper -> Rat -> Snake -> Owl
DAV Class 6 Science Chapter 1 notes on Our Environment
Nature tries to maintain a balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide. explain it with a figure
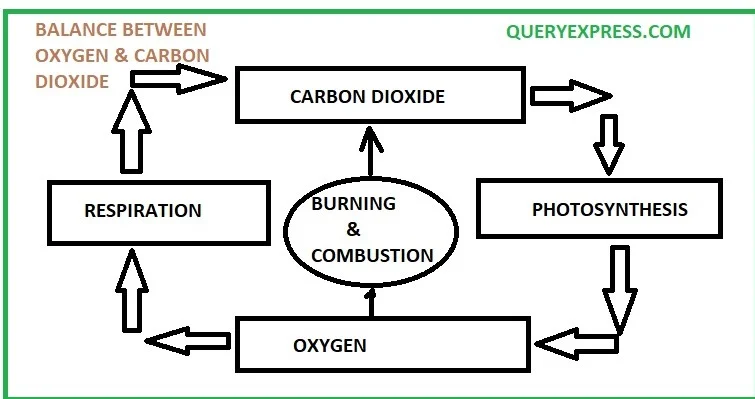
- Respiration and Burning: Both plants and animals constantly take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide during respiration. Additionally, the burning of wood, coal, and petrol adds more carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. This process increases the level of carbon dioxide in the air.
- Photosynthesis: To counteract the rise in carbon dioxide, plants use it to make their own food through photosynthesis. During this process, which happens in the presence of light, plants consume carbon dioxide and release oxygen back into the atmosphere.
Nature maintains a balance between the amount of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere through the processes of respiration, burning, and photosynthesis.
- All living organisms respire all the time, taking in oxygen and giving out carbon dioxide.
- Carbon dioxide is also added to the atmosphere through the burning of wood, coal, and petrol.
- Plants use up carbon dioxide and give out oxygen during the process of photosynthesis, which takes place in the daytime.
- This cycle ensures a balance is maintained between the two gases in the atmosphere.
The Mineral Cycle, Dav class 6 science chapter 1 notes
mineral cycle.
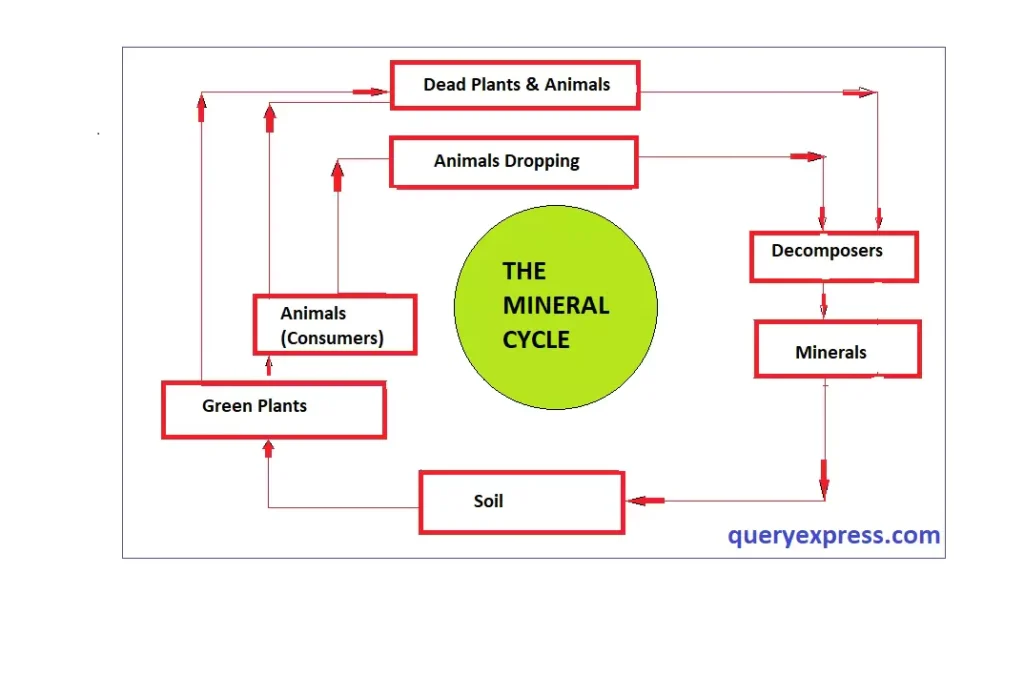
- The abiotic substances supply nutrients to the producers.
- Producers, which are plants, prepare food for the consumers, which are animals.
- When both producers and consumers die, decomposers break them down into simpler substances.
- These nutrients then return to the soil, air, and water.
- These nutrients are used again by new producers, and the whole cycle repeats continuously.
Download the Dav class 6 Science book
Also Read
